关于3D Printing in China / 中国的3D打印市场,3D科学谷在德国D1G1TAL杂志上发表了独家的看法。以下为发表所提交的英文文章,D1G1TAL杂志发表了德文翻译文章。
(D1G1TAL杂志的印刷版本和在线电子版本均为收费阅读方式,受出版约束,在此,3D科学谷仅分享英文部分)
![]() Brief look at the state of additive manufacturing in and from China
Brief look at the state of additive manufacturing in and from China
Looking East and anticipating developments in China especially in manufacturing and machinery, has been a must-do for a long time now. It is not surprising that the buzz around digitization, additive manufacturing and 3D printing we have here, has taken center stage in our outlook on China as well. 3D printing is still considered to be an emerging, however global development and is characterized by multiple technological approaches and fast changes.
Where do 3D printing application, technology and machinery stand in China? Who are the players and what are the developments that are relevant for us in Europe today or very soon? It is not easy to tell from the outside. From an inside perspective, we would like to shed some light on the state of the Chinese 3D printing industry,thetechnology and industrial application development in China. While the industry might in average be very young in China, we would like to show that there is also a range of companies that has been active in this market for a longer time and introduce a wide range of examples of technological achievements of international relevance and scale.
![]() The big leap: nearly half of 3D printing enterprises have entered the market in 2016 or after
The big leap: nearly half of 3D printing enterprises have entered the market in 2016 or after
Various 3D printing technologies have emerged over the recent years in the Chinese market. From stereolithography to selective laser melting, selective laser sintering, LENS technology, bio-printing technology, electron beam technology and even ultrasonic welding–basically all major 3D printing technologies are represented domestically. The biggest leap in industrial development has been recorded from the year 2016 onward: 46.9% of all companies which entered the 3D printing market in China have done so as from 2016. However, there has been already a range of Chinese companies active in this industry even before 2010. We could call those companies “veteran players”, considering thatwe are talking about a still emerging industry. Among those are Shaanxi Hentong,Beijing Longyuan,Shanghai UnionTech, Wuxi Easyway, to name just a few.
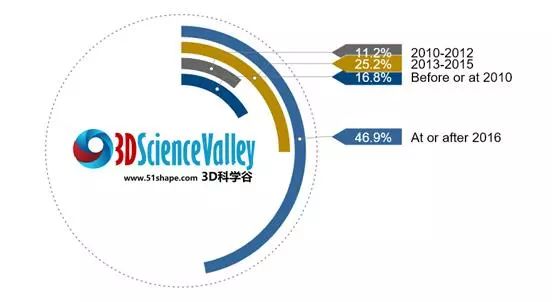
Chart 1: Majority of companies entered the 3D printing market after in or 2016
(Source:China 3D printing service market – White Paper by 3D Science Valley,to be published in March 2018; data pool at TCT Shanghai / data pool: survey & market research conducted by 3D Science Valley)
Two major government support programs for the additive industry
The recent market growth has been fueled by two major government initiatives. The “Additive and Laser Manufacturing R&D Project (2016-2020)” has been launched by the Ministry of Science and Technology. The program supported 27 different projects with funds of around 36 million USD in 2016 and planned to support another 19 to 38 projects with approximately 101 million USD in 2017.
Recently, the “Action Plan for Additive Manufacturing Industry Development (2017-2020)”was issued jointly by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and 12 other departments in December 2017. The plan has clearly put forward that by 2020 the annual sales revenue of China’s additive manufacturing industry shall exceed 3.17 billion USD, with an average annual growth rate of more than 30%. Key core technology development is to be synchronized with the international level.
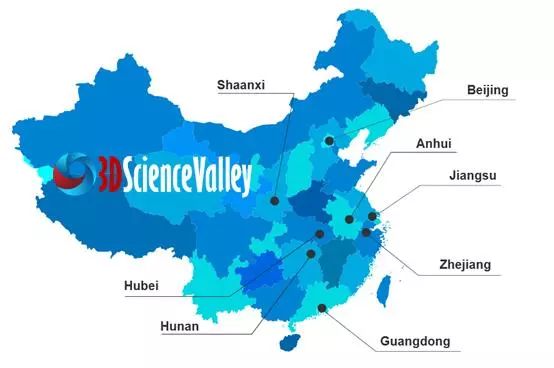
![]() Industry Clusters
Industry Clusters
Image:3D printing industry clusters China;
image courtesy:Designed by Katemangostar / Freepik, Adjusted by 3D Science Valley
The geography of the market: 3D Printing Industry Clusters in China
Industry clusters are mainly found in Shaanxi, Hubei, Beijing, Jiangsu, Hunan, Zhejiang, Guangdong, and Anhui. In addition to the general suspects, logically linked to the industrial conglomerations on the East coast around the capital Beijing and industrial hubs of Shanghai)Anhui, Jiangsu, Zhejiang) and Guangdong, there are also clusters to be found further West, with the Shaanxi Cluster being of special interest.
Wuxi Falcontech and Beijing AMC powders are currently the major metal powder producers in China. Xi’an Bright Laser is the market leader for metal 3D printing equipment and printing services.
For plastic 3D printing services, Dongguan Keheng Prototyping and Wuxi Eastway are ahead of the competition. Shanghai UnionTech has the largest market share instereolithography equipment in China.
Shaanxi
Powered by the Xi’an Jiao Tong University and Northwestern Polytechnical University the area is home turf of one of the seasoned and most advanced players in the market, metal printer manufacturer and 3D printing sales, service and development provider Xi’an Bright Laser. Most importantly it sports the National Additive Manufacturing Innovation Center. Supported by the Ministry of Industry, the National Additive Manufacturing Innovation Center is hosted by the Xi’an Institute Corporation of Additive Manufacturing in Xi’an.The central government has granted funds of 200 million RMB (31.5 million USD) to the Innovation Center.
Hubei
Huazhong University of Science and Technology is at the heart of this regional cluster around the city of Wuhan. Wuhan is the capital city of HuBei province, and Hu Bei Province is one of the industry cluster of automotive industry. The most established printer manufacturer stemming from this cluster is Wuhan Huake, which is a spin-off of Huazhong University of Science and Technology. One of the investors of Wuhan Huake is Huazhong Numerical Control, which is strong in the traditional manufacturing market.
Beijing
The capital’s cluster evolved mainly aroundthe Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics and Tsinghua University. Typical companies from the area are Beijing TierTime or Longyuan.Tiertime is specialized in desktop 3D printers and is aggressively expanding the international market with 70% of the sales revenue originating from outside of China. Longyuan has gained attention of the market with its sand mould production using SLS technology.
Jiangsu
Shanghai and Jiangsu, the province neighboring Shanghai towards the north and west, are home of 3D printer manufacturers Shanghai UnionTech (stereolithography industry veteran) andPrismlab among others. The cluster hosts a whole range of additive manufacturing service providers such as Ureal 3D, Sunshine-Laser, Shanghai Tolerance, Road Ahead, Shanghai Bluebird, and others.Ureal 3D,for instance, has paved their way with a clear market positioning by providing 3D printing service focused on conformal cooling in metal moulds.
Hunan
The major brand from the mainly automotive industry driven Hunan cluster in middle China is Farsoon. Founded in 2009 and headquartered in the city of Changsha, Farsoon is active internationally offering printers for both polymer and metal processing. In Europe,the brand is known through it’s more recent partnership with Prodways (since 2015). Further by partnering with BASF, Farsoon also provides nylon powder for SLS systems.
Zhejiang
The cluster in the South of Shanghai formed around Zhejiang University. Most prominent playerfrom the region is Shining 3D. Shining 3D has built up wide ranging competence in 3D printing systems, 3D printing education and 3D printing service. The company offers 3D scanners, desktop 3D printers, selective melting systems as well as bio-printers.
Guangdong
The southern cluster around Hongkong and Shenzhen hosts companies such as Zhuhai CTC, Hanbang, SYNDAYA and HansLaser. Currently HanBang is more focus on dental applications based on its selective laser melting technology. Zhuhai CTC, with their root in DLP technology, now also has entered the selective laser melting systems market. HansLaser, which is a major competitor to Trumpf in the laser welding and laser cutting industry, now also penetrated the 3D printing market with its own selective laser melting and DLP technology.
Anhui
The region west of Shanghai is home of 3D printing company HengLi and the Anhui ChunGu 3D printing industry cluster close to the city of Wuhu. Anhui is one of the automotive industry clusters in China. Those 3D printing companies emerged in the area are trying to serve the automotive industry with prototyping services and applied research on light weight designs.
![]() Select notable technology developments for 3D printing made in China
Select notable technology developments for 3D printing made in China
DED technology
In the field of DED technology (direct energy deposition), Professor Zhang Hai’ou from the Huazhong University of Science and Technology announced in 2016 a breakthrough in research and development of a metal 3D printing technology called “smart micro-forging”. This technology is competitive with the technology of US based company Sciaky. Its major benefit is to increase part strength and toughness, an improved product lifecycle as well as higher reliability of the process. According to its developers, smart micro-forging can also be used to create thin-walled metal components, resultingin a reduction of excess material and lower equipment costs.
Nano 3D printing
BMF Material Technology is a Boston/Shenzhen-based startup firm that manufactures nano or micro 3D printers and materials, as well as custom products for other companies using its equipment.Companies such as BMF are crucial in bringing nano 3D printing technology to a new level with printers that have micrometer/nanometer resolution and the capacity to perform high-volume manufacturing. What sets BMF apart, according to MIT technology review , is the equipment’s level of rigor and the exceptional choice of materials and processes. BMF’s precision 3D printing technology can produce small mechanical and highly complicated parts with examples ranging from tiny springs or special electrical connector shapesto cardiac stents.
Bio-material printing
In 2017, Regenovo from Hangzhou unveiled the bio-architect X 3D bio-printer for the mass production of human tissue. The bio-architect X is an extension ofone of the product lines Regenovo developed. Previously, Regenovo had released the Bio-Architect–Lite, Bio-Architect–Pro, and Bio-Architect–WS systems. The bio-architect X is China’s first high-throughput 3D bio-printer for mass producing.
Simulation methods & special alloys
Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics is at the forefront in academic research of numerical simulation methods for: active tracking of the solidification behavior of the laser 3D printing melting pool, for the laser-powder and particle-optical coupling process as well as laser 3D printing composite material such as special alloys and composites.
![]() Industry research in application technology
Industry research in application technology
Many Chinese 3D printing companies are involved in industry research on application technology and part design. We selected a range of technically advanced and internationally competitive examples of their developments.
Application technology: Complex thin-walled or lightweight parts for Aerospace
One of the challenges in metal printing is toapply selective laser melting technology for manufacturing large and complex thin-walled parts. Stress, deformation and metallurgical defects are the major factors that plague the industry when it comes tothose parts.Xi’an Bright Laser has made series of breakthrough application developments in this area. Typical parts are:

Component: Fan blade
Size: 1200mm
Material: Titanium alloy
Print time: 120h
Image courtesy: Xi’an Bright Laser

Component: thin-walled ring component
Size: Diameter 577mm x 80mm
Material: high temperature alloy
Print time: 18h
Image courtesy: Xi’an Bright Laser
A minimum wall thickness of only 0.3mm has been achieved. The successful completion of the blade edge has proven that Xi’an Bright Laser achieved a new level in application technology. To achieve such results, it is necessary to understand the material, the process and to have the appropriate quality of machinery in place. The leaf ring was manufactured by 4 lasers simultaneously, which is another example howthe company handled the challenge of cracking, a problem with all 3D printed large thin-walled components.
The China Academy of Space Technology has gainedmany years of experience in 3D printing, especially regarding design for additive manufacturing (DfAM).The academy has developed a systematic approach for the study of lattice cell structures for lightweight satellite components, and with this has achieved to be internationally competitive in this field.

Component: cubic satellite internal structure component with internal lattice structure designed by China Academy of Space Technology
Size envelope: 380 × 380 × 380mm (printed in several parts)
Wall thickness:0.5mm
Materials: AlSi10Mg
Image courtesy: Xi’an Bright Laser
Application technology: medical implants
In commercialized medical implant printing, currently Beijing AK Medical is the Chinese market leader. In August 2015,AK Medical received the CFDA (National Food and Drug Administration) approval for its 3D ACT artificial hip joint system based on 3D metal printing technology.
In July 2016, AK Medical was awarded the approval of the State Food and Drug Administration (CFDA) for a vertebral cage based on 3D ACT technology. It is also the first metal 3D printed interbody fusion cage product licensed by the CFDA in China. 3D ACT technology is a combination of various technologies from clinical medicine, computer technology, material science and mechanical design, such as Electron Beam Molten Metal 3D Printing Technology (EBM) andprecision 3D reconstruction technology.
Application technology: Conformal cooling in molding
For the mold industry,Xi’an Bright Laser has worked on mold flow analysis, flow channel design as well as3D print parameter development, mold printing, and finally3D printing mold processing.Using the BLT-S200 / S310 equipment,they debugged special printing parameters for conformal cooling in mold production. Furthermore, with the H13, 18Ni300 (MS1), 17-4PH, G05 and others, special mold materials were developed. After heat treatment, those reached hardness of up to HRC50 or more.
Application technology:Stereolithographyprototyping system for the shoe industry
Shanghai UnionTech launched a 3D printing system tailored to the shoe industry. Using stereolithography technology (SLA), UnionTech’s FM700 system is the world’s first dual galvanometer light curing 3D printing system for the footwear industry and was formally introduced to the footwear market in April 2017. The use of dual-laser and high-speed variable spot technology is defining here. This way printing of 0.06mm details of the soles and side patterns are possible. In terms of efficiency, the FM700 system’s efficiency increased by 4 times compared to ordinary light-cured 3D printers.
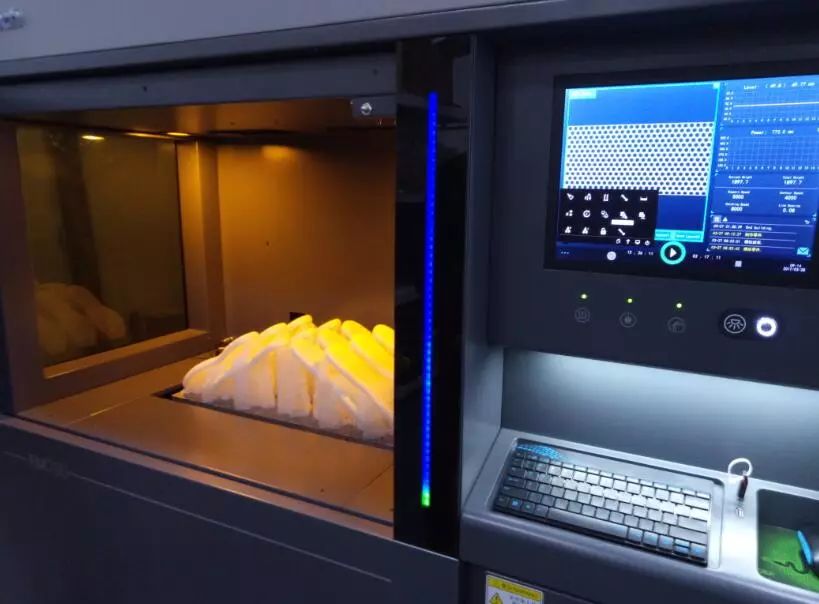

Image: UnionTech FM700, image courtesy UnionTech
Application technology: Bio-3D printing of membranes
MEDPRIN’s first product ReDura® is a biomimetic-synthetic-absorbable duralsubstitute with CE and CFDA registration certificates. The material has been widely applied in more than 30 countries on tens of thousands of cases, and is considered as the dura mater (ridge) membrane closest to a patient’s autologous cells with the best repair effect.
![]() China’s 3D printing industry’s road ahead – Bridging the gap
China’s 3D printing industry’s road ahead – Bridging the gap
Currently the Chinese market is still lacking regarding industrialized applicationsthat could compare to iconic achievement such as the 3D printed fuel nozzle of GE, the Adidas shoe middle sole, and Siemens’ turbine blade. However, China has developed its own strengths in 3D printing technology and applications, which we hope we were able to highlight. Those achievements and most importantly future developments are further fueled bygovernmental support to this industry. The Chinese 3D printing industryhas gained attentionacross the countryis starting to attract investors worldwide, which is testament to its potential.
We see a lot of room for improvement to catch up to the trend of industrialization of 3D printing as on international level. One key point is the connection of the 3D printing and manufacturing industries – an issue that applies globally. Still, it seems especially difficult for 3D printing companies in China to reach out to the local manufacturing industry. In China today,relatively few companies are aware of the power of 3D printing and the Chinese market lacks the openness and the understanding for the role this technology can play. This is because till recently, China focused on low value added manufacturing, while this is not the strength of 3D printing. Though this is clearly changing, this heritage created a gap which is very noticeable today and probably reason for the high export shares in revenue for many Chinese 3D printing companies.
Essentially, the manufacturing industry of China will need to understand the power if 3D printing to create manufacturing and product life cycle value as they upgrade from a low to a high(er) value added manufacturing philosophy. Bridging the gap will be key for the 3D printing industry to reach maturity and scale in China.
![]() About the authors
About the authors
Wang Xiaoyan/Kitty (China) is an analyst and consultant focused on the 3D printing industry. She is founder of 3D Science Valley, the leading Chinese information and exchange platform on industrial 3D printing. 3D Science Valley has furthermore published a range of whitepapers on the industrial application of 3D printing, a book on 3D printing for the Automotive industry and provides customized analysis and consulting services to the industry and the local government in China.Co-Author Korinna Penndorf (Germany/UK) is the Europe Correspondent for 3D Science Valley.
资料下载,请加入3D科学谷3D产业链QQ群:529965687
更多信息或查找往期文章,请登陆www.51shape.com,在首页搜索关键词
网站投稿请发送至2509957133@qq.com